Nanoparticles and quantum dots as emerging optical sensing platforms for Ni(II) detection: Recent approaches and perspectives.
S. Naithani, Heena, P. Sharma, S. Layek, F. Thetiot,* T. Goswami,* S. Kumar,* Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 2025, 524, 216331. DOI: 10.1016/j.ccr.2024.216331
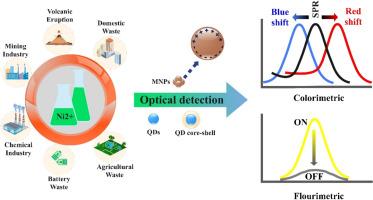
Over the preceding years, nickel (Ni) and its compounds have been increasingly employed in various aspects of human social life, metallurgical/industrial manufactures, healthcare and chemical processes. Although Ni is considered as an essential trace element in biological system, excessive intake or metabolic deficiency of Ni2+ ions may cause detrimental health effects to the living organisms. Therefore, a facile and accurate detection of Ni2+, especially in environment and biological settings, is of huge significance. As an efficient detection method, assaying Ni2+ using optical (colorimetric and/or fluorogenic) sensors has experienced quite a vigorous growth period with large number of excellent researches. Nanomaterial-based optical sensors including metal nanoparticles (MNPs), quantum dots (QDs), and carbon dots (CDs) offer distinct advantages over conventional small-molecule organic and inorganic sensors. This study mainly provides an overview of the recent advancements and challenges related to the design strategies of various optical nanosensors to selectively detect Ni2+ ion. Emphasis has also been placed on comparing the sensing performance of various nanosensors along with exploring future perspectives.